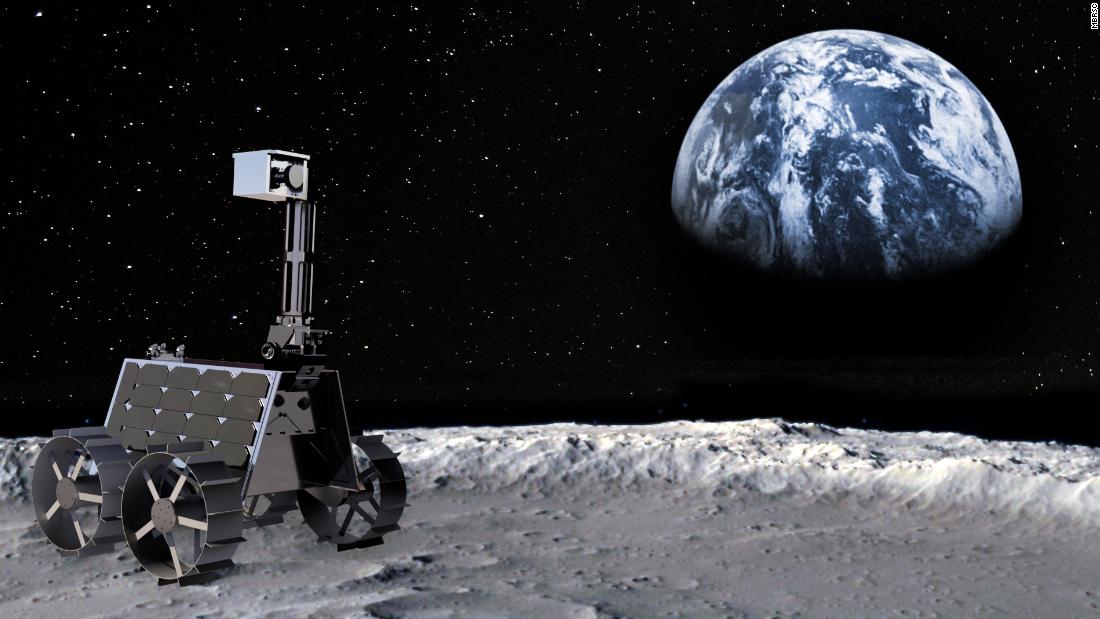
The UAE has announced a monthly mission that will use an unusually small rover, with only four wheels and a weight of 10 kilograms (22 kilograms).
The rover, which will be built in Dubai, is much smaller than the last rover successfully deployed on the moon; Yutu-2 from China has six wheels and weighs 140 kilograms.
By comparison, Curiosity, NASA’s only active rover on Mars, is even bigger – it weighs 899 kilograms (1,982 kilograms) the size of a small SUV.
The UAE is trying to join an elite club of just three countries – the US, Russia and China – to successfully land a spacecraft on the lunar surface. In 2019, the Indian mission Chandrayaan-2 landed on the moon. Here you can see his rover on a ramp moving in the main vehicle before launch.
China’s Yutu-2 is the only active monthly rover, but NASA wants to add its own. Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, or VIPER, is a mobile robot that will wander around the south pole of the moon in search of water ice.
VIPER, about the size of a golf cart, is being tested at NASA’s simulated monthly operations lab in Ohio.
Star trackers helped position the Hope spacecraft in orbit.
The Hope spacecraft was launched from the Tanegashima Space Center in southwestern Japan. The United Arab Emirates has not yet announced partners for the rocket or launch pad for its 2024 monthly unmanned mission.
AlMansoori (L), presented here with the reserve astronaut of the Sultan AlNeyadi mission, also had to master the incredibly complex systems inside the Soyuz capsule. Both astronauts had to learn Russian to operate on it.
Bjarke Ingels Group (BIG) architects designed a city prototype for humans to live on Mars and then adapted the design for the Emirate desert.
The design consists of biodomes, each covered with a transparent polyethylene membrane.
The design has floodlights full of water, which on Mars would protect the inhabitants from radiation, while allowing light to enter the rooms.
The BIG design for the Earth-related City of Science sets aside areas for Mars life research, including the cultivation of food on the red planet.