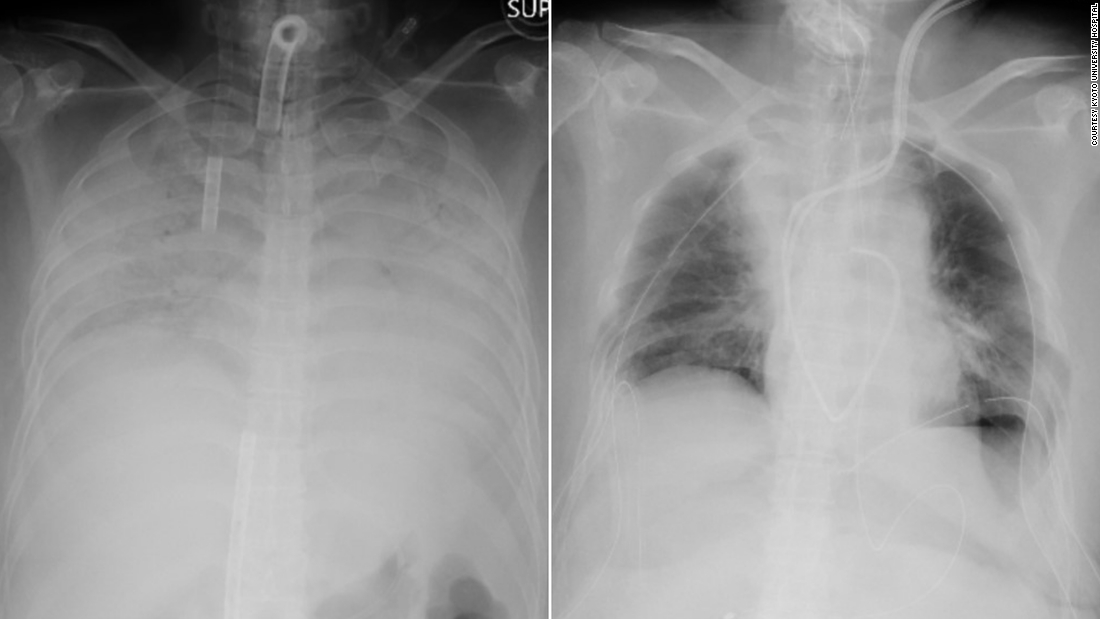
Kyoto University Hospital said the woman underwent an 11-hour operation on Wednesday by a 30-person medical team for a lung tissue transplant from her husband and son.
But the Kyoto hospital said the case was the first in which lung tissue was transplanted from living donors to a patient with Covid-19.
Dr. Hiroshi Date, a thoracic surgeon at the hospital that conducted the operation, said he gave hope to patients suffering from severe lung damage from Covid-19.
“We have shown that we now have a lung transplant option (from living donors),” he told a news conference Thursday.
The patient, identified only as a woman in the western Kansai region of Japan, contracted Covid-19 late last year and spent months on a life support device that functioned as an artificial lung, according to Kyoto University Hospital.
Covid-19 caused so much damage to his lungs that he was no longer functional and needed a lung transplant to survive.
The woman’s husband and son offered to donate parts of her lungs. Transplants from brain-dead donors are still rare in Japan, and living donors are considered a better option, according to the hospital.
The husband and son are in a stable condition, and the woman remains in intensive care. He is expected to be able to leave the hospital in about two months, according to the hospital.